Test automation can dramatically reduce testing costs, with some organisations seeing reductions of up to 40%, according to the Capgemini World Quality Report of 2023. However, the financial benefits are not uniformly distributed across industries. As test automation becomes more widespread, understanding where it delivers the greatest return on investment (ROI) and the factors influencing these outcomes is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance their software development processes.
Rising Adoption and Accelerated Release Speeds
Test automation has gained significant traction among organisations. Seventy-four percent of entities have adopted test automation to some extent, as per the Capgemini World Quality Report 2023. This widespread implementation is driven by the substantial uptick in software release speeds, which Forrester Research indicates can increase by 40-70% through automation. Test automation allows software teams to execute tests far more rapidly than traditional manual testing, thus facilitating more frequent updates and releases.
Automated tests can run 80-90% faster than manual tests, according to Gartner’s findings in 2021. The acceleration in testing not only saves time but also enhances the reliability and frequency of software deliveries, providing a dual benefit of quicker product availability and improved customer satisfaction.
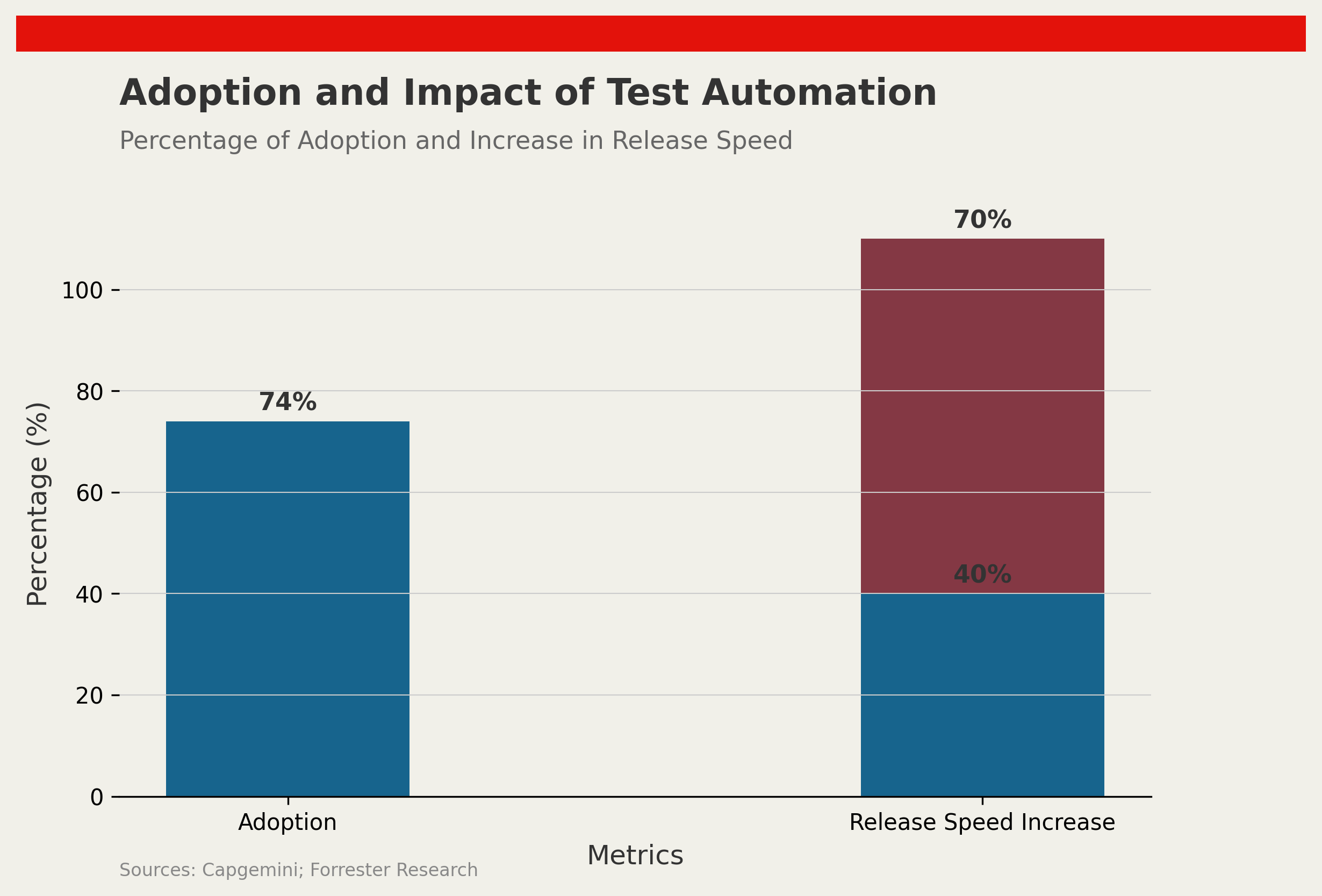
As the chart shows, the adoption of test automation and the increase in release speed are significant factors driving the technology’s integration into organisational workflows.
The Economic Imperative
The financial allure of test automation lies not just in its potential to cut implementation costs but also in its ability to generate long-term savings through efficiency. Test automation reduces the duration and labour associated with testing cycles. These efficiencies translate directly into reduced project timelines and lower personnel costs, with Forrester suggesting possible test cost reductions of up to 40%.
Moreover, the ability to release software more quickly represents an opportunity cost that should not be underestimated. Faster releases mean companies can capture market demand more agilely, stay ahead of competitors, and respond swiftly to customer feedback or changes in the marketplace. This agility is a critical competitive edge for businesses in fast-moving sectors like software development.
Varied Impact Across Industries
Despite its advantages, the benefits of test automation are not uniformly felt across all sectors. Industries dealing with hardware or embedded systems, where testing protocols are often complex and varied, may find the initial setup and maintenance costs of automation tools could eclipse potential savings. In such cases, the specificity and variability of test requirements might demand a hybrid approach, integrating both manual and automated testing methods to optimise outcomes efficiently.
For these industries, the scalability and repeatability that automation offers might be less impactful than in purely software-based environments. As such, businesses must carefully consider their operational context and testing requirements before making substantial investments in test automation technologies.
Future Prospects
As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities and applications of test automation. The continued development of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) promises even greater efficiencies and the potential to automate more complex testing scenarios. However, this progress will likely require a shift in how companies perceive and implement automated testing strategies, particularly concerning the integration of AI-driven capabilities.
Test automation’s future will see it adapting to more intricate testing environments and industries with specific demands. While today, AI can assist in testing by reducing redundancy and increasing accuracy, future iterations are poised to tackle challenges that currently necessitate human intervention. Companies that embrace these advancements will likely gain a significant competitive edge, transforming test automation from a tactical asset to a strategic imperative.
References
- Capgemini World Quality Report, World Quality Report 2023, Capgemini, 2023
- Forrester Research, The State of Test Automation, Forrester, 2022
- Gartner, Automated Testing Insights, Gartner Research, 2021