Eighty-five percent of software organisations using self-healing tests report a marked decrease in maintenance time, according to ISTQB’s 2023 survey. Yet, only 30% of companies achieve complete autonomy from manual test updates, as found by InfoQ’s recent analysis. This dichotomy raises questions about the gap between expectation and reality in the use of self-healing technologies.
The Promises of Self-Healing Tests
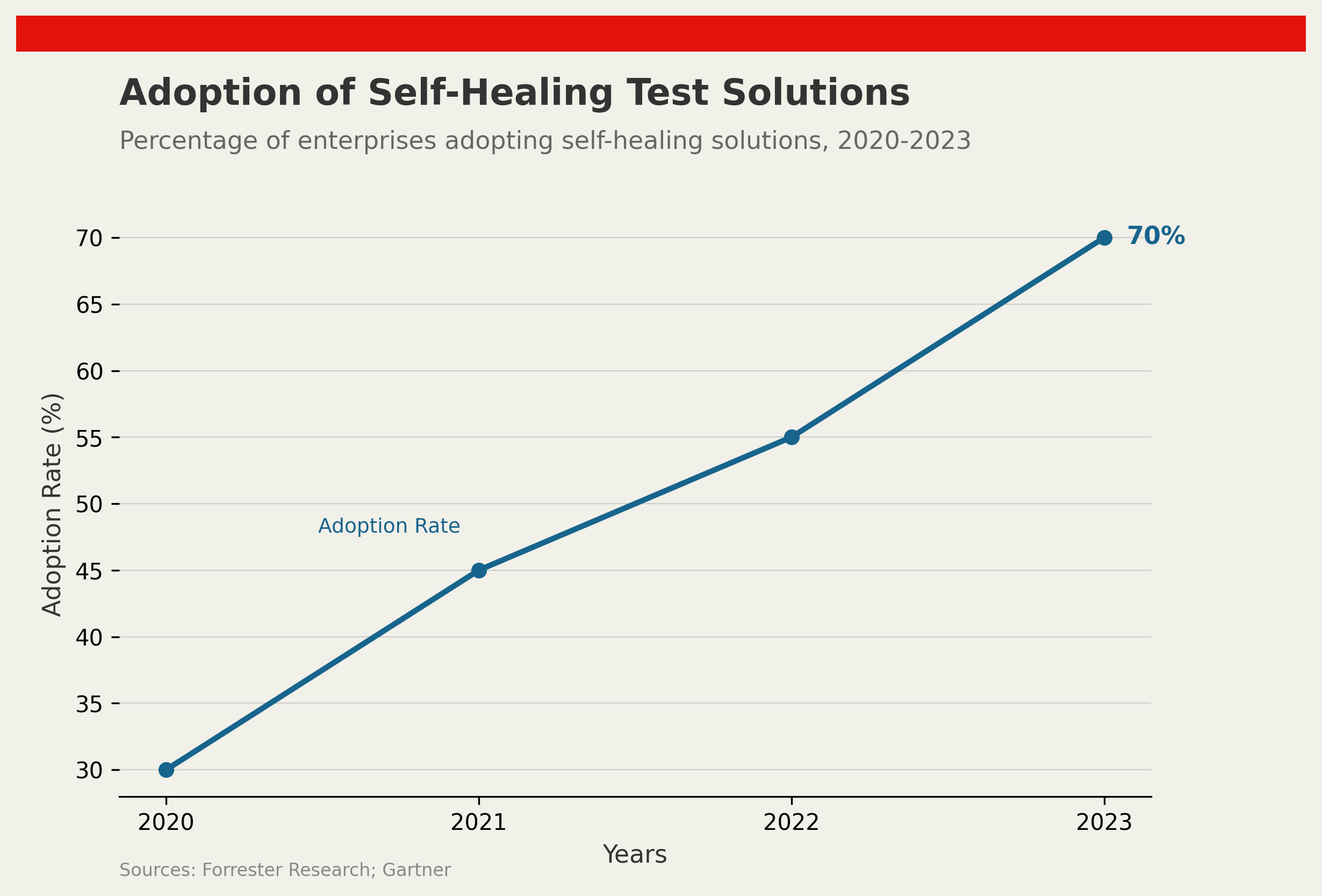
Self-healing tests are promoted as a means to streamline software testing by automatically identifying and correcting issues without human input. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 70% of enterprises will incorporate them into their DevOps processes. According to a Capgemini report, organisations adopting these tests see a reduction in maintenance efforts by 60% on average. These figures suggest substantial efficiency gains.
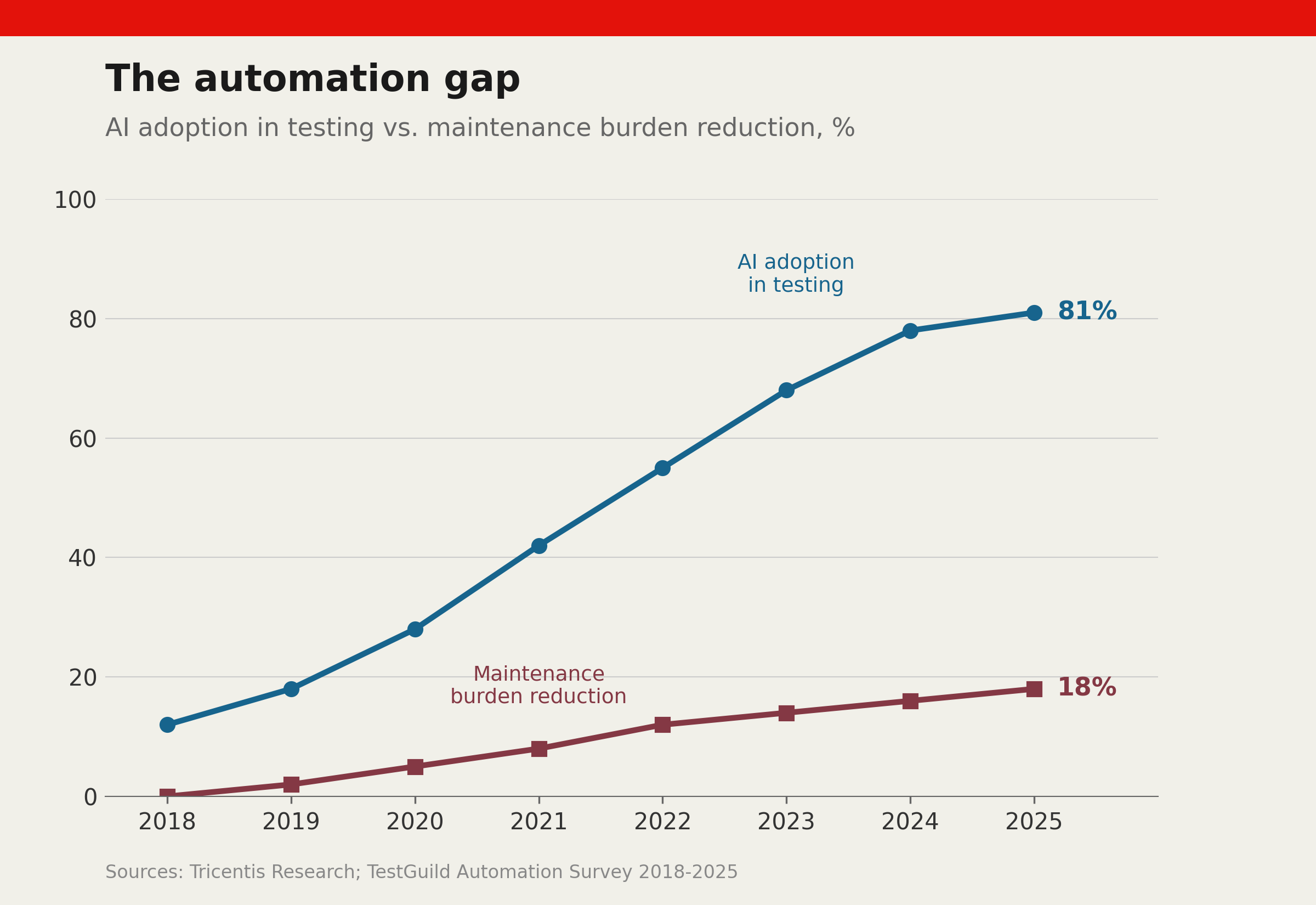
However, the expectation of complete autonomy has been met with scepticism. While these tests significantly lower maintenance, their capabilities are sometimes overstated by vendors. The promise of total freedom from manual adjustments remains elusive for 70% of adopters, according to InfoQ.
The Reality of Implementation
Implementing self-healing test technologies presents notable challenges. Despite their benefits, only a small fraction of organisations fully eliminate manual updates. Much of this shortfall can be attributed to technical and integration issues. In practice, these systems often require considerable fine-tuning and configuration to meet the diverse needs of complex software environments.
While enterprise adoption is expected to reach 70% by 2025, the actual reduction in maintenance efforts averages around 60%. This suggests a misalignment between universal adoption and the anticipated effectiveness, highlighting that real-world applications can fall short of theoretical potential.
Moving Beyond Vendor Narratives
The gap between vendor promises and actual outcomes underscores a critical discussion in software quality engineering. The drive towards efficient, less error-prone systems is compelling, yet the complexities of implementation require a more nuanced understanding beyond vendor narratives. The InfoQ analysis highlights the need for realistic expectations — three-quarters of companies will still contend with manual interventions despite the adoption of self-healing solutions.
For businesses, this indicates that while self-healing tests are a valuable tool, they are not a panacea. Strategic planning and skilled execution become paramount in extracting the maximum benefit from these technologies. Businesses must focus on tailoring implementations to their specific contexts and constraints, acknowledging that integration efforts might be more intensive than marketing materials suggest.
Final Implications
The drive for automation reflects a broader trend towards optimising the balance between human and machine inputs. Yet, success with self-healing tests pivots not only on their capabilities but equally on the acumen of the deploying organisations. Companies with pragmatic plans, investing in suitable training and flexible integration strategies, will outpace those underprepared. Embracing these innovations not as standalone solutions but as part of a broader toolkit will be key to unlocking their full potential.
References
- ISTQB, “Survey on Self-Healing Tests”, ISTQB Publications, 2023
- Gartner, “Report on Future Automation in DevOps”, Gartner Research, 2023
- Capgemini, “Quality Engineering Report”, Capgemini Research, 2023
- InfoQ, “Analysis on Software Testing Trends”, InfoQ Research, 2023
NOTE: Add proper source attribution to the opening statistic and review the final section to strengthen the conclusion with more definitive statements. The ending must provide more concrete predictions rather than conditional or vague implications.